An ENT specialist (Ear, Nose, and Throat specialist), also known as an otolaryngologist, is a medical doctor who specializes in diagnosing and treating conditions that affect the ears, nose, throat, and related structures of the head and neck. ENT specialists are trained to handle a wide variety of medical and surgical conditions involving these areas.
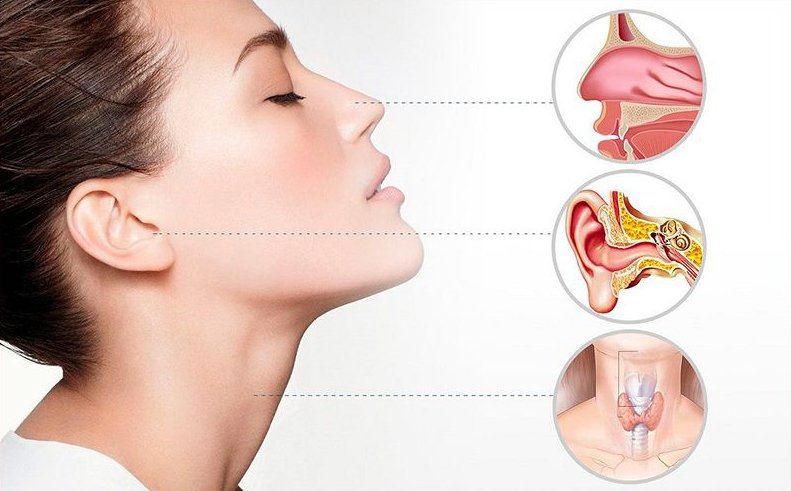
Key Areas of Expertise for an ENT Specialist:
- Ear (Otology):
- Hearing Loss: Evaluation and treatment of various types of hearing loss (sensorineural, conductive, or mixed).
- Ear Infections: Conditions like otitis media (middle ear infection) or otitis externa (outer ear infection).
- Tinnitus: Ringing in the ears, often caused by noise exposure, ear infections, or other conditions.
- Balance Disorders: Issues like vertigo or dizziness, often caused by problems with the inner ear.
- Earwax Impaction: Removal of excessive earwax, which can cause discomfort and hearing loss.
- Nose (Rhinology):
- Sinusitis: Inflammation of the sinuses, which can be acute or chronic and may cause facial pain, nasal congestion, and headaches.
- Allergies: Diagnosing and treating allergic rhinitis, which causes sneezing, nasal congestion, and runny nose due to allergens like pollen, dust, or pet dander.
- Nasal Polyps: Growths in the nasal passages that can cause blockages, leading to breathing difficulties or sinus infections.
- Deviated Septum: A condition where the nasal septum (the partition between the nostrils) is crooked, potentially leading to breathing problems.
- Snoring and Sleep Apnea: ENT specialists help diagnose and treat issues related to snoring and obstructive sleep apnea, which involves the airway becoming blocked during sleep.
- Throat (Laryngology):
- Voice Disorders: Conditions such as hoarseness, vocal cord nodules, or laryngitis that affect the quality of the voice.
- Swallowing Problems (Dysphagia): Difficulty swallowing caused by various conditions, including structural issues or neurological conditions.
- Tonsil and Adenoid Issues: Infections or enlargement of the tonsils and adenoids, especially common in children, which may require surgical removal (tonsillectomy or adenoidectomy).
- Laryngeal Cancer: Cancers that affect the larynx (voice box), often treated by surgery, radiation, or a combination of therapies.
- Reflux: Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) or laryngopharyngeal reflux (LPR) can lead to throat irritation, hoarseness, or swallowing difficulties.
- Head and Neck (Head and Neck Surgery):
- Thyroid Disorders: Conditions like hypothyroidism, hyperthyroidism, or thyroid cancer that affect the thyroid gland, which is located in the neck.
- Head and Neck Cancer: Diagnosis and surgical treatment of cancers in the mouth, throat, larynx, or neck, including skin cancers, lymphomas, and squamous cell carcinomas.
- Salivary Gland Disorders: Problems with the salivary glands, including infections, stones, or tumors.
- Facial Trauma: Surgical management of facial injuries, including fractures of the jaw, nose, or facial bones.
Common Procedures Performed by ENT Specialists:
- Ear Procedures:
- Myringotomy: A small incision in the eardrum to relieve pressure or drain fluid (often used to treat middle ear infections).
- Tympanoplasty: Surgery to repair a perforated eardrum.
- Cochlear Implants: Surgically implanted devices that help restore hearing in individuals with severe hearing loss.
- Ear Tube Insertion: A procedure to insert small tubes into the eardrum to prevent fluid buildup and recurrent ear infections.
- Nose Procedures:
- Septoplasty: Surgical correction of a deviated septum to improve nasal airflow.
- Endoscopic Sinus Surgery: Minimally invasive surgery to remove blockages or polyps from the sinuses using a small camera (endoscope).
- Rhinoplasty: Cosmetic or reconstructive surgery to reshape the nose or correct structural abnormalities.
- Sinus Surgery: Procedures to treat chronic sinusitis or nasal polyps, often involving the removal of obstructions in the sinus passages.
- Throat Procedures:
- Tonsillectomy and Adenoidectomy: Surgical removal of the tonsils and/or adenoids, often performed in children with recurrent infections or sleep apnea.
- Laryngoscopy: A procedure to visualize the larynx (voice box) and vocal cords using a flexible camera.
- Vocal Cord Surgery: Surgical treatment of vocal cord nodules, polyps, or other growths that affect the voice.
- Thyroid Surgery: Removal of part or all of the thyroid gland due to disorders such as cancer, goiter, or hyperthyroidism.
- Head and Neck Procedures:
- Thyroidectomy: Removal of part or all of the thyroid gland, often due to cancer or benign conditions.
- Neck Dissection: Surgical removal of lymph nodes or tissues in the neck to treat cancer.
- Salivary Gland Surgery: Removal of tumors or stones from the salivary glands.
- Reconstructive Surgery: Surgical reconstruction following trauma or cancer surgery, particularly for the face, neck, or head.
When to See an ENT Specialist:
You may need to see an ENT specialist if you experience symptoms related to the ears, nose, throat, or head and neck that are persistent, recurring, or severe. Common reasons to visit an ENT include:
- Ear Problems: Hearing loss, ear pain, ringing in the ears (tinnitus), or balance issues (vertigo).
- Nasal Issues: Chronic sinusitis, frequent nosebleeds, stuffy or blocked nose, allergies, or difficulty breathing through the nose.
- Throat Issues: Persistent sore throat, hoarseness, difficulty swallowing, or lumps in the neck or throat.
- Sleep Apnea or Snoring: Issues with breathing during sleep, such as loud snoring, choking, or gasping for air.
- Head and Neck Problems: Lumps or growths in the neck or mouth, thyroid problems, or unexplained pain in the face or neck.
Training for ENT Specialists:
Becoming an ENT specialist involves several years of medical education and training:
- Medical School: As with all physicians, ENT specialists must first complete medical school, which typically takes 4 years after earning an undergraduate degree.
- Residency: After medical school, ENT specialists undergo a 5-year residency program that includes clinical training in the diagnosis, treatment, and surgery of ear, nose, and throat conditions.
- Board Certification: After completing residency, ENT specialists can earn board certification by passing an exam from a professional organization, such as the American Board of Otolaryngology.
- Fellowship (optional): Some ENT specialists choose to pursue further subspecialization in areas such as pediatric otolaryngology, head and neck surgery, or facial plastic surgery.
